AI in 3D Printing: From Generative Design to Predictive Maintenance
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer just optimizing code or automating workflows—it’s revolutionizing how we design, prototype, and manufacture. Without AI in 3D printing, it was once limited by manual adjustments and trial-and-error processes, is now evolving through AI-powered precision, predictive analytics, and generative design. The result? Smarter, faster, and more adaptable production techniques that are reshaping industries.
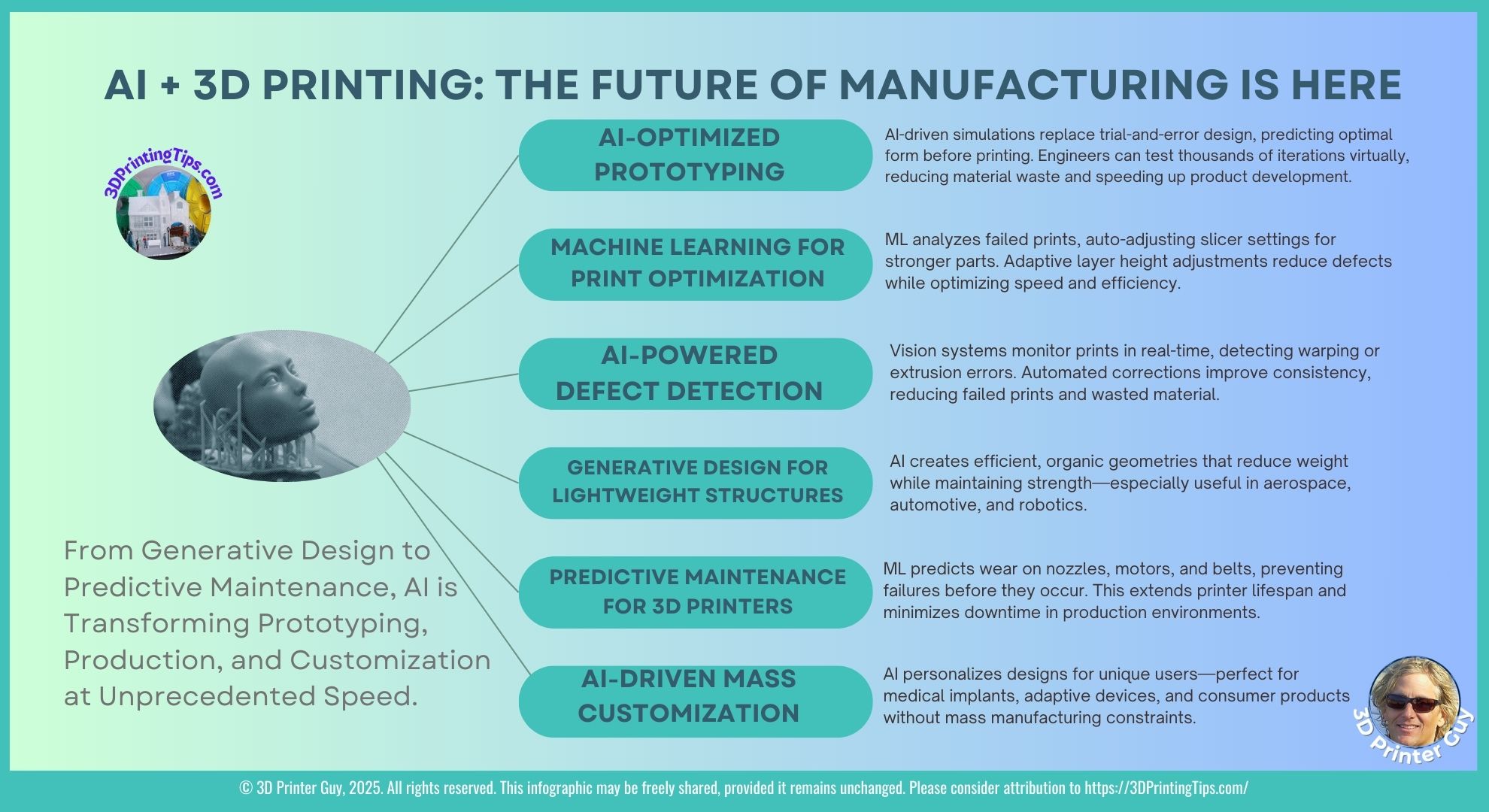
1️⃣ AI-Optimized Prototyping: Smarter Design, Faster Iterations
Traditional prototyping often involves multiple iterations, manual adjustments, and extensive testing before arriving at a final design. AI in 3D printing is changing this by enabling virtual simulations that predict optimal forms before printing.
- Generative AI for Design Exploration AI-driven topology optimization refines designs by analyzing stress points and material distribution. Engineers can test thousands of iterations virtually, reducing material waste and speeding up product development.
- Digital Twins for Real-World Testing AI-powered digital twins allow engineers to simulate real-world conditions before printing, ensuring that designs meet performance requirements without physical testing.
- AI-Assisted CAD Tools AI-powered CAD assistants suggest design improvements based on historical data and industry standards, helping engineers create stronger, more efficient models.
2️⃣ Machine Learning for Print Optimization: Smarter Slicing
AI in 3D printing is transforming slicer software, making it more adaptive and efficient. Instead of relying on static presets, machine learning algorithms analyze past print failures and adjust slicer settings dynamically.
- Predictive Print Failure Analysis AI can predict print failures by analyzing past errors and adjusting slicer settings dynamically. This reduces wasted material and improves print success rates.
- Real-Time Adaptive Slicing AI-driven adaptive slicing modifies layer height mid-print based on geometry complexity, ensuring optimal resolution without unnecessary print time.
- AI-Optimized Infill Strategies AI-powered infill algorithms optimize strength while reducing printer filament material usage, ensuring lightweight yet durable prints.
3️⃣ AI-Powered Defect Detection: Real-Time Corrections
One of the biggest challenges of AI in 3D printing is print defects—warping, extrusion errors, and adhesion failures. AI-powered vision systems monitor prints in real-time, detecting issues before they ruin an entire print job.
- Thermal Imaging for Overheating Detection AI-driven thermal cameras detect overheating issues before they cause warping, ensuring consistent print quality.
- Automated Print Monitoring AI-powered camera systems track extrusion consistency and pause prints if anomalies are detected, preventing wasted material.
- Self-Healing Algorithms AI-driven self-healing algorithms adjust nozzle temperature and extrusion rates to compensate for minor defects, improving print reliability.
4️⃣ Generative Design for Lightweight Structures: AI-Driven Efficiency
Generative design is one of AI’s most exciting applications in 3D printing. Instead of manually designing parts, AI creates efficient, organic geometries that reduce weight while maintaining strength.
- Aerodynamic Optimization AI can simulate aerodynamic properties, making it invaluable for drone and automotive applications.
- Multi-Material Optimization AI ensures strength while reducing weight in critical areas, optimizing material usage.
- Bio-Inspired Designs AI mimics nature’s efficiency, leading to stronger yet lighter structures.
5️⃣ Predictive Maintenance for AI in 3D Printing: AI as a Technician
AI is revolutionizing printer maintenance, predicting wear on components before failures occur.
- Component Wear Forecasting AI can forecast component wear based on usage patterns, preventing unexpected failures.
- Automated Calibration Routines AI-driven auto-calibration ensures consistent print quality without manual intervention.
- AI-Powered Supply Chain Management AI predicts filament depletion and orders replacements proactively, reducing downtime.
6️⃣ AI-Driven Mass Customization: Personalized Manufacturing
AI is enabling mass customization, allowing users to create personalized designs without mass manufacturing constraints.
- User Preference Analysis AI can analyze user preferences to generate unique designs tailored to individual needs.
- Automated Scaling Algorithms AI adjusts designs for different body types in medical applications.
- AI-Powered Marketplaces AI-driven marketplaces allow users to customize and order 3D-printed products with minimal human intervention.
7️⃣ Ethical Considerations & Future Trends
As AI in 3D printing continues to evolve, it’s important to consider ethical implications and future trends.
- AI Bias in Design How do we ensure AI-generated models are inclusive and functional for all users?
- Sustainability in AI-Driven 3D Printing Can AI help reduce waste and improve material efficiency?
- The Future of AI in Additive Manufacturing What’s next? AI-driven self-repairing materials and autonomous print farms.
Final Thoughts
AI-driven 3D printing is no longer futuristic—it’s happening now. Whether you’re designing products, optimizing workflows, or exploring automation, the intersection of AI and manufacturing is reshaping possibilities.
Here are 5 more ways AI is affecting the 3D printing industry.
How do you see AI influencing your industry? Drop your thoughts in the comments or let’s start a deeper conversation.
🔹 #AIinManufacturing 🔹 #AdditiveManufacturing 🔹 #GenerativeDesign 🔹 #3DPrinting