3D printing temperature issues troubleshooting
1. Introduction
Temperature control is one of the most critical factors in achieving successful 3D prints. 3D printing temperature issues troubleshooting identifies how filaments melt, adhere, and solidify, shaping the outcome of every design. However, even small deviations in temperature can lead to frustrating issues like warped layers, stringing, or poor adhesion.
This 3D printing temperature issues troubleshooting article aims to empower readers to identify and resolve temperature-related problems in 3D printing. By understanding the role of temperature and using practical troubleshooting techniques, hobbyists and professionals alike can improve print quality and reliability.
2. Importance of Temperature in 3D Printing
Temperature plays a pivotal role in determining the success of a 3D print. It controls how filament transitions from solid to liquid and back to solid, ensuring proper adhesion and structural integrity. When temperatures are not carefully managed, issues such as layer separation or print failure can arise.
Each filament type—such as PLA, ABS, PETG, and nylon—has unique temperature requirements. PLA generally prints at lower temperatures, while materials like ABS demand higher heat for both extrusion and bed adhesion. Understanding these requirements allows users to optimize their settings for specific projects.
Moreover, consistent temperature control contributes to:
- Improved print quality, reducing defects like warping and stringing.
- Enhanced strength and durability of printed parts.
- Reliable adhesion between layers, preventing cracks or weak spots.
3. Common Temperature-Related Issues
Temperature mismanagement can lead to a variety of 3D printing challenges. Here are the most frequent problems and their potential causes:
- Under-Extrusion or Over-Extrusion
- Symptoms: Gaps in layers (under-extrusion) or excess filament blobs (over-extrusion).
- Causes: Incorrect nozzle temperature, filament flow issues, or slicer misconfigurations.
- Layer Adhesion Problems
- Symptoms: Weak bonding between layers, leading to cracks or separation.
- Causes: Insufficient nozzle temperature or poor heat consistency during printing.
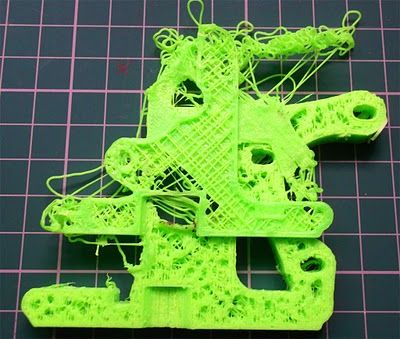
- Stringing and Oozing
- Symptoms: Fine threads of filament stretching between parts of the print.
- Causes: Overheated nozzle or insufficient retraction settings.
- Warping and Cracking
- Symptoms: Edges of the print lifting off the bed (warping) or visible cracks in higher layers.
- Causes: Improper bed temperature, uneven cooling, or environmental drafts.
- Clogged Nozzle
- Symptoms: Little to no filament extrusion during printing.
- Causes: Debris or degraded filament caused by incorrect nozzle temperature.
- Heat Creep
- Symptoms: Filament softening above the hot end, leading to jams.
- Causes: Overheating in the cold end of the printer.
4. Diagnosing Temperature Issues
Accurate 3D printing temperature issues troubleshooting diagnosis is the first step in resolving temperature-related problems. Here’s how users can identify and analyze these issues:
- Observe Print Behavior
- Watch for symptoms like stringing, layer gaps, or warping during printing.
- Monitor any signs of filament under- or over-melting.
- Control the Environment
- Ensure the printer is in a stable, draft-free area to prevent environmental temperature fluctuations.
- Use an enclosure for materials sensitive to cooling, such as ABS or nylon.
- Run Test Prints
- Print calibration objects, like temperature towers, to pinpoint the optimal nozzle and bed temperatures for the filament.
- Adjust settings incrementally to isolate the source of the problem.
- Inspect Hardware
- Check the condition of key components like thermistors and heating elements.
- Ensure no loose connections are affecting temperature consistency.
- Log Observations
- Keep notes on the symptoms and changes made during troubleshooting.
- Refer back to these records for recurring issues or when working with similar materials.
5. Solutions and Best Practices
Here are actionable strategies to tackle temperature-related issues in 3D printing:
- Calibrate Nozzle and Bed Temperatures
- Use manufacturer guidelines as a starting point, and print temperature towers to fine-tune settings for your filament.
- Gradually adjust temperatures and observe changes in extrusion and layer adhesion.
- Optimize Cooling Settings
- Balance fan speed to suit material needs; for instance, PLA requires active cooling, while ABS benefits from reduced airflow.
- Ensure uniform cooling across layers to avoid warping.
- Upgrade Hardware
- Consider investing in high-quality thermistors and hotends for accurate and stable temperature control.
- Use heated beds and enclosures to maintain consistent environmental conditions.
- Monitor and Adjust Mid-Print
- Check print progress periodically to identify any signs of temperature issues.
- Pause and modify settings mid-print if abnormalities arise.
- Proper Filament Storage
- Store filaments in airtight containers with silica gel to prevent moisture absorption, which can disrupt extrusion and heating.
These practical 3D printing temperature issues troubleshooting tips should help ensure smoother and more reliable 3D printing.
6. Advanced Tools for Temperature Management
Incorporating advanced tools can greatly enhance temperature control and diagnostics in 3D printing. Here are some to consider:
- Temperature Towers for Calibration
- Print a temperature tower to identify the ideal nozzle temperature.
- This tool helps visualize how different settings affect adhesion, finish, and extrusion.
- Slicer Software Features
- Leverage advanced slicer settings, such as variable temperature zones for different layers.
- Explore features like “Cooling Overrides” for better control during specific print phases.
- Thermal Imaging Cameras
- Use thermal imaging to spot inconsistencies in heat distribution.
- Particularly useful for diagnosing uneven bed heating or cooling issues.
- PID Tuning
- Perform PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) tuning on your printer to stabilize hotend and bed temperatures.
- Many printers offer this option in their firmware or control interface.
- Temperature Monitoring Devices
- Attach external thermometers to cross-check temperature accuracy.
- Useful for double-checking calibration and identifying faulty sensors.
7. Preventative Measures
Taking proactive steps regarding 3D printing temperature issues troubleshooting can minimize the occurrence of temperature-related issues and ensure consistent 3D printing results. Here are some key measures:
- Regular Maintenance
- Clean the nozzle and hotend regularly to prevent clogs caused by degraded filament residue.
- Check and replace worn-out thermistors, heater cartridges, or other critical components.
- Create and Use Filament Profiles
- Develop specific settings for each type of filament, including nozzle and bed temperatures, cooling speeds, and retraction distances.
- Save these profiles in your slicer software for quick application.
- Avoid External Temperature Fluctuations
- Use an enclosure to shield the printer from drafts or changing ambient conditions.
- If possible, keep the printer in a climate-controlled environment.
- Store Filament Properly
- Store spools in airtight containers with silica gel to prevent moisture absorption, which can affect extrusion and heat stability.
- Pre-Print Preparation
- Conduct a pre-print check to ensure settings are correct for the selected filament and print design.
- Run small test prints to confirm calibration before starting long or complex projects.
By adopting these preventative measures, users can ensure smoother and more reliable printing experiences.
8. Frequently Asked Questions about 3D printing temperature issues troubleshooting
Here are some common questions about temperature issues in 3D printing and their quick resolutions:
Q: What should I do if my first layer isn’t sticking to the bed?
- Answer: Check the bed temperature and ensure it matches your filament type. For materials like PLA, a bed temperature of 60°C is usually effective. Also, verify that your bed is leveled and clean, as residue can interfere with adhesion.
Question: Why does my filament burn or produce a bad smell while printing?
- Answer: Overheating is likely the cause. Reduce the nozzle temperature to the lower range recommended for your filament and ensure proper airflow in your workspace.
Q: How can I stop stringing between parts of my print?
- Answer: Increase retraction settings in your slicer to prevent filament from oozing during movement. If stringing persists, lower the nozzle temperature slightly.
Question: What causes prints to warp or crack?
- Answer: Warping often results from uneven cooling or a cold bed. Use an enclosure to maintain consistent ambient temperature and consider increasing the bed temperature for better adhesion.
Q: How can I identify a clogged nozzle?
- Answer: If the filament isn’t extruding properly or you notice gaps in your print, the nozzle may be clogged. Clean it with a needle or use cold-pull techniques to remove residue.
Question: What is heat creep, and how can I prevent it?
- Answer: Heat creep occurs when filament softens prematurely due to overheating in the cold end of the printer. Ensure proper cooling of the heat sink and avoid prolonged printing at high temperatures.
Q: Should I pause a print if I notice temperature issues?
- Answer: Yes, if the issue is causing visible problems in your print, pause and adjust settings. Many printers allow you to modify temperature mid-print to recover quality.
Question: Why does the first few layers of my print look uneven?
- Answer: Uneven first layers often stem from improper bed leveling or inconsistent nozzle temperature. Double-check your leveling setup and ensure the nozzle temperature aligns with your filament’s requirements.
Q: What should I do if the filament keeps jamming?
- Answer: Filament jams are commonly caused by heat creep, incorrect extrusion settings, or poor filament quality. Ensure your printer’s cooling setup is working properly and that the filament is stored in a dry environment.
Q: My printer stops extruding mid-print—what’s wrong?
- Answer: This can result from a clogged nozzle or degraded filament. Pause the print, inspect the nozzle for blockages, and use high-quality filament that hasn’t absorbed moisture.
Question: What happens if the bed temperature is too high or too low?
- Answer: A bed that’s too hot can cause the filament to warp or stick excessively, while a cold bed may prevent adhesion. Adjust the temperature based on filament guidelines and use adhesives like glue stick or tape if needed.
Q: Can I print with different filaments at the same time?
- Answer: Yes, but this requires careful temperature management for each filament type. Dual-extrusion printers with independent hotends can help accommodate differing temperature settings.
9. 3D printing temperature issues troubleshooting Conclusion
Managing temperature effectively is crucial to the success of any 3D printing project. From ensuring optimal nozzle and bed temperatures to diagnosing and addressing common issues like stringing, warping, and heat creep, the right approach can significantly enhance print quality and reliability. By using advanced tools, adopting preventative measures, and staying proactive with maintenance, 3D printing enthusiasts can overcome temperature challenges with confidence.
Remember, troubleshooting is an iterative process—experiment, refine, and keep learning from each print. With consistent effort, temperature control can become second nature, paving the way for creative and precise results.
[sibwp_form id=2]

-
🆚 Prusa vs Creality: Comparing Popular 3D Printer Brands
A concise comparison of Prusa and Creality—exploring brand philosophy, hardware, user experience, and long-term value to help you choose the right 3D printer.
-
Best 3D Printers for Kids and Families in 2025: A Safety-First, Feature-Rich Comparison
When it comes to choosing the best 3D printer for kids and families (including your teens), safety, ease of use, and creative potential are key priorities.
-
Common FDM printer troubleshooting tips
Troubleshooting an FDM 3D printer starts with identifying the root cause of print failures.
-
Affordable resin printers for beginners
1. Why Choose Resin Printing as a Beginner? Are you looking for an Affordable resin printers for beginners? For newcomers to 3D printing, resin printers offer exceptional detail and smooth surface finishes, making them ideal for models, miniatures, and intricate designs. Unlike filament-based (FDM) printing, resin printers use UV light to cure liquid resin layer…